Harmful algal blooms occur annually in Western Lake Erie

Harmful algal blooms plague Western Lake Erie every year. Factors that affect the location and severity of blooms include rainfall, water temperature, wind, and nutrient inputs. Warm, wet years produce larger blooms as precipitation washes nutrients into the lake. Early warming can cause blooms earlier in the year which may result in smaller blooms that last longer.
Windy conditions can mix lake waters and move algae around, reducing the overall severity of blooms by diffusing the effects. 2018 was an unusual year, with an early bloom onset and strong westerly winds that resulted in the bloom being pushed offshore into the eastern islands region (Bass Islands). From year to year there is a lot of variability in conditions, which lead to more or less severe blooms. Future blooms can be diminished if there are less nutrient inputs from commercial fertilizers and manure.
In an effort to assess annual bloom severity, the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has developed a standarized method for assessing algal bloom severity. The Bloom Severity Index is based on the bloom biomass– the amount of algae–over a sustained period, usually 30 days of peak bloom, which normally occurs in July or August. This method does not take into account algal bloom toxicity, but a score of 5 or greater is considered a potentially harmful bloom.
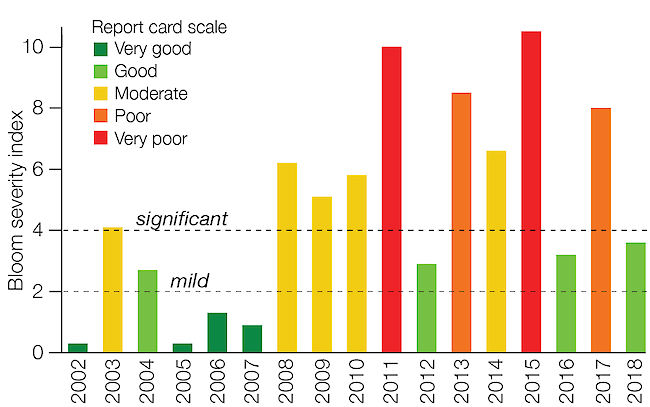
Annual variability in weather conditions cause bloom severity to fluctuate from year to year, as illustrated in the graph above. For example, 2011 and 2013 had severe summer blooms while the 2012 bloom was a mild bloom on the severity index scale. Future blooms can be diminished if there is less nutrient pollution from commericial and residential fertilizers and manure, reducing blooms even in years with high rainfall.
Conditions in Sandusky Bay differ from the rest of the basin

Sandusky Bay is a unique system within the larger Lake Erie basin, largely due to its isolation from the open waters of Western Lake Erie. The shallow Bay is ringed by rich coastal wetlands that provide habitat for fishes and other animals, trap nutrients in the soil, and reduce the effects of wave action within the Bay.
In addition to its productive fisheries, Sandusky Bay provides opportunities for outdoor recreation and tourism. Cedar Point, Sandusky Bay, and the surrounding areas are known as the “Vacationland” region of Ohio.
Excessive nutrient and sediment loading, low flows, and algal blooms have resulted in a reduction of water quality in Sandusky Bay. There is an almost year-round (March–December) bloom of the cyanobacteria Planktothrix in Sandusky Bay. Unlike the open waters of Western Lake Erie, nitrogen levels in the bay tend to be low, especially in the late summer. When algal blooms caused by excess nutrients die off, they are eaten by bacteria, which create oxygen-free (anoxic) conditions. This results in almost constant internal phosphorus loading when phosphorus is released from anoxic sediments.
Reducing nutrient inputs from the Maumee River will improve Western Lake Erie health

The Maumee River has the largest watershed of any Great Lakes River, covering 8,316 square miles (21,540 km2). It drains portions of Indiana, Michigan, and Ohio before entering Western Lake Erie at Maumee Bay in Toledo, Ohio, a city with a population of nearly 300,000. Fort Wayne, Indiana, with a population of over 250,000, sits at the start of the Maumee River, where the St. Joseph and St. Marys rivers come together.
In addition to the large metropolitan areas at either end of the watershed, nearly two-thirds of the Maumee River watershed is used for agriculture. While the Maumee River only contributes 5% of the flow into Lake Erie, it contributes over 40% of the phosphorus load. This phosphorus load comes primarily from commercial fertilizers and manure as well as residential lawns. The phosphorus washes into Western Lake Erie at Maumee Bay, which tends to be the epicenter of large annual algal blooms. Because of this, the Maumee River watershed is the priority watershed targeted in the Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement. This bi-national agreement seeks to reduce the phosphorus inputs to Western Lake Erie by 40% to maintain healthy levels of algal growth and support a productive Lake Erie ecosystem. Reducing nutrients will improve water quality and habitat for fish and other wildlife. It will also have a positive impact on drinking water supplies and recreational opportunities.
