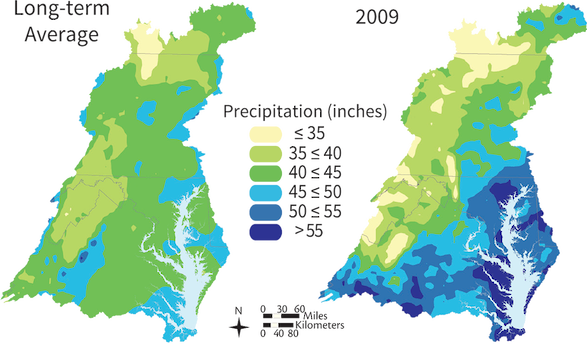
The overall health of Chesapeake Bay in 2009 was the best it has been since 2002, based on an assessment using water quality and biotic indicators. In 2009, the unique precipitation pattern provided insights into the relative roles of nutrient and sediment inputs that affect Bay health, from the great Susquehanna River to the smaller tributaries in Maryland and Virginia. Although Pennsylvania and New York received relatively low amounts of precipitation, tributaries adjacent to the Bay received unusually high levels of precipitation.